DISC Behavior Graph
DISC Behavior Styles
DISC is a theory about behavior styles. Psychologist William Moulton Marston created the DISC behavior system in the 1920s and wrote about them in his book, The Emotions of Normal People. Under the name Charles Moulton, Marston also created super hero Wonder Woman.
In Marston’s DISC descriptions
“D” stands for Dominance
“I” stands for Inducement
“S” stands for Submission
“C” stands for Compliance
Marston did not copyright his theory, so people have been modifying it for decades, including changing the names of the behavior styles. This website uses:
Dominance
Influence
Steadiness
Conscientiousness
Behavior Styles, Not Personality Styles
William Mouton Marston wrote about “behavior styles,” not “personality styles.”
This website uses “behavior styles” because the clues are behavior clues.
Behavior clues are easy to recognize.
Is There A Best Behavior Style?
No behavior style is best.
Each behavior style has success characteristics and failure characteristics.
Each behavior style is good at something the other three behavior styles have trouble doing well.
DISC Behavior Clues
Marston based his behavior styles on observable behavior. The observable behavior is based on four clues: tone of voice, words, pace, and body language.
Tone of voice Loudness or softness, variety of pitch, ease or hesitancy of speech
Frequently used words Used repeatedly in different conversations and situations
Pace of speech and movement How fast or slow someone moves and speaks
Body language Handshakes, eye contact, facial expressions, gestures
High D Dominance
Tone of voice is a moderate range of pitch, clear, confident, may be loud, may sound forceful.
Words include results, productivity, control, success, goals, now, challenge, win, lead, new, benefits, bottom line. .
Pace is fast, talking fast and moving quickly and decisively.
Body language is purposeful with lots of hand movements while talking, some big gestures.
High I Influence
Tone of voice is flowing with lots of variation, may be loud, dramatic variety in pitch.
Words include fun, recognition, ideas, feel, party, enthusiastic, exciting, spotlight, names.
Pace is fast, talking fast and moving quickly and spontaneously.
Body language is dramatic, expressive face, lots of hand and arm gestures with whole body movement at times.
High S Steadiness
Tone of voice is soft and warm, little variety in pitch, may be hesitant.
Words include family, promise, help me, guarantee, think about it, attention, relationship, routine, logical, trust, security.
Pace is slow, talking slowly and moving with a steady ease.
Body language includes hand gestures, close to the body arm gestures, and small changes in facial expression.
High C Conscientiousness
Tone of voice is moderate in volume and controlled with very little variety in pitch.
Words include facts, proven, procedure, rules, analyze, guarantee, plan, thoughts, credibility, accuracy, preparation, think it over, risk, based on the data.
Pace is slow, talking slowly, moving with a slow and methodical pace. .
Body language is minimal with few changes in expressions.
DISC Behavioral Factors
Each behavior style focuses on a different behavioral factor — problems, people, pace, or procedure.
Dominance Factor Problems
How we respond to problems and challenges
How we use power
Influence Factor People
How we attempt to influence other people
How we interact with other people
Steadiness Factor Pace
How we respond to the pace of our surroundings
How we respond to change
Conscientiousness Factor Procedure
How we respond to rules and procedures
How we respond to authority
DISC Emotional Traits
Each behavior style also has an emotional trait.
High D Dominance Anger
High I Influence Trust
High S Steadiness Selective about sharing their feelings
High C Conscientiousness Fear
Shorthand DISC Descriptions
You can use these shorthand descriptions to quickly identify your own and other people’s High DISC behavior style.
High D Dominance
Outgoing
Gets things done
High I Influence
Outgoing
Connects with people
High S Steadiness
Reserved
Connects with people
High C Conscientiousness
Reserved
Gets things done
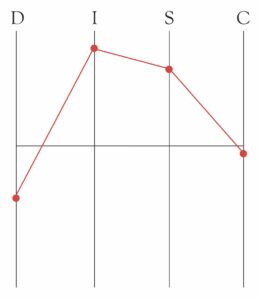
Plotted Graph
DISC behavior styles can be graphed in great detail with a plotted graph plus explanations. Search online for “free DISC profile assessment” to get your own profile / assessment. You could get more than one free profile to compare them.
Many of the companies providing free profiles / assessments use the phrase “personality test.” I use the phrase “behavior styles” because that is what William Mouton Marston used. The clues to the styles are behavior clues. See the clues above.
This is Paula M. Kramer’s plotted DISC graph.
Shorthand Graph
A shorthand graph will give you a general understanding about your behavior style blend. Knowing how to create a shorthand graph for yourself should help you create shorthand graphs for people you want to understand better. Using DISC behavior styles and Spranger guiding values, I now understand every relationship in my life.
Most people will have two behavior styles above the midline and two behavior styles below the midline.
High/Secondary High
Low/Secondary Low
Some people will have three behavior styles above the midline and one behavior style below the midline.
High/Secondary High/Tertiary High
Low
Some people will have one behavior style above the midline and three behavior styles below the midline.
High .
Low/Secondary Low/Tertiary Low
Be honest when you fill out the shorthand graph. It’s all right to be better at getting things done than at connecting with people. Just learn to connect with people so you can be better at getting things done.
3 Behavior Styles Above The Midline
If you have three behavior styles above the midline, determining your Secondary High behavior style is more complicated. You may have to think about it for a while before you figure it out. Your Secondary High behavior style will play a bigger part in your life than the other behavior style above the midline.
If you have three behavior styles above the midline and you have figured out your High and Secondary High behavior styles, you have nothing else to figure out. The third behavior style above the line is your Tertiary High behavior style. Your Low behavior style is the one behavior style below the midline.
/ /
1 Behavior Style Above The Midline
If you have one behavior style above the midline, your Secondary behavior style (the one that modifies your High behavior style the most) is a Low behavior style.
Your modifying Low behavior style is the one that has more meaning in your life than the other two behavior styles below the midline. You may have to think about your three Low behavior styles for a time to figure out which one is Secondary and which one is Tertiary. Your Tertiary style has the least meaning in your life.
Shorthand Graph Example
Paula M. Kramer is a High I Influence because she talks fast, uses dramatic body language, and wants to influence people with her ideas. She Secondary High Steadiness because she needs self-determined routines and quiet times. Those routines and quiet times help her maintain stability in her personal and professional relationships.
As for Paula’s Low behavior styles, cooperating with other people (Low D Dominance) is almost continuously important to her. She takes charge of situations only if cooperating looks impossible or difficult and it seems that no one else knows enough to take charge. When Paula takes charge, I tries to do so in a cooperative way unless other people resist her efforts to be cooperative.
As for Paula’s Low C Conscientiousness, whether or not she follows rules and procedures depends on the situation and the authority involved. If Paula feels respect from an authority, she will respect that authority and follow rules and procedures. If Paula does not feel respect from an authority, she will make her own rules and procedures out of respect for herself.
Cooperating with other people to solve problems is a continuing need for Paula. Following rules is not a continuing need for Paula. Creating her own rules is not a continuing need for Paula. Her Low D Dominance has more meaning in her life than her Low C Conscientiousness, so her D is lower than her C, meaning it is stronger than her C. D Dominance is Paula’s Low behavior style and C Conscientiousness is her Secondary Low behavior style.
Paula’s shorthand graph is:
I/S
D/C
Shorthand DISC Graph Worksheet
We are all combinations of all four behavior styles. We cannot have both the High and Low characteristics at the same time for any behavior style. We have either the High or Low characteristics for each behavior style.
Remember, though, that if you have trouble choosing between the High and Low characteristics for one behavior style, you probably go back and forth between the High and Low characteristics of that behavior style. That behavior style is situational for you. In a detailed graph, your situational behavior style would be close to the midline.
Decide which High and Low behavior style characteristics describe you when you are feeling comfortable and safe.
Fill in the appropriate graph on the next page.
High D
Copes with challenging situations by taking charge
Fast anger fuse
Low D
Copes with challenging situations by looking for ways to cooperate with others
Slow anger fuse
High I
Feels comfortable with people
Optimistic and trusting
Low I
Feels cautious about people
Pessimistic and skeptical
High S
Functions best following the steady pace of self-determined routines
Keeps emotions inside
Low S
Functions best with frequent changes of pace
Expresses emotions freely
High C
Respects authority
Fears breaking authority’s rules and procedures
Low C
Ignores authority
Fearlessly breaks authority’s rules and procedures
Adapted Behavior Styles
We also have several adapted behavior styles that help us create success in particular situations. Think about a continuing situation in which you don’t feel comfortable and safe.
Do you take control even though you feel uncomfortable taking control?
Your adapted behavior style in that situation is High D Dominance.
Do you try to think up ideas when you normally wait for others to think up ideas?
Your adapted behavior style in that situation is High I Influence.
Do you to try please someone more than you normally try to please people?
Your adapted behavior style in that situation is High S Steadiness.
Do you follow the rules more carefully than you normally do?
Your adapted behavior style in that situation is High C Conscientiousness.
Creating Shorthand Graphs For Other People
To determine someone else’s shorthand behavior style graph, follow the same steps.
Satisfy the behavior style needs of other people only in the ways that leave you feeling safe and respected.
Do not allow other people to manipulate you into questionable actions. Listen to positive words you can trust.
Satisfy the behavior style needs of other people for their sake, not for your sake.
Never assume that you can change the behavior style blend of another person.
© Paula M. Kramer, 2020 to the present
All rights reserved.
Updated March 22, 2025.